2025-04-20
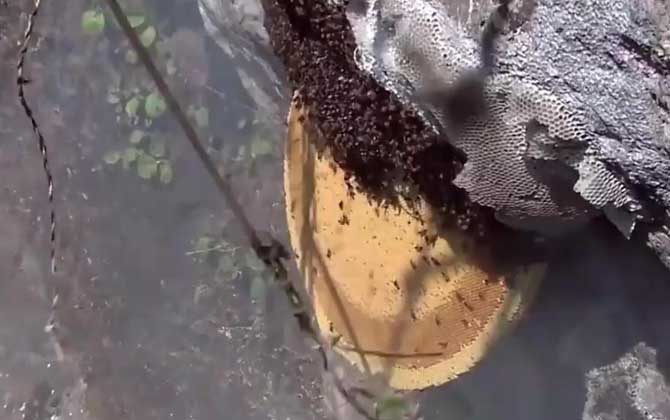
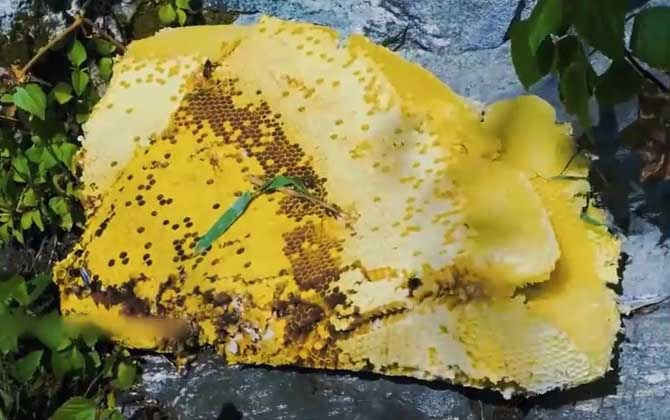
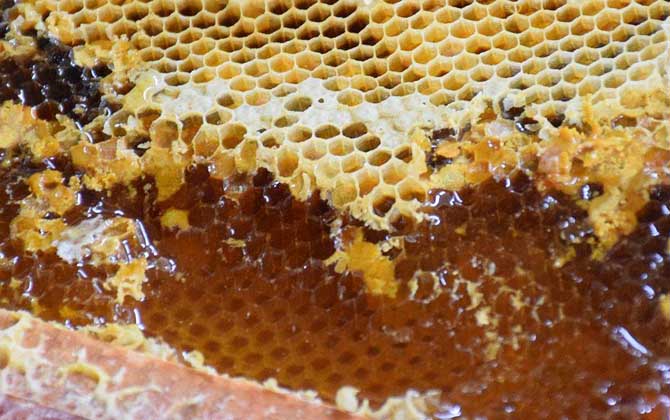
Beekeeping: Costs, Profits, and Key Considerations Beekeeping has become a profitable venture for many mountain farmers, offering significant income opportunities. However, success varies widely—while some thrive, others face financial losses. Calculating costs and potential profits is crucial for sustainable beekeeping. Below, we analyze the economics of beekeeping in detail. 1. Initial Investment Costs Starting a beekeeping operation involves these primary expenses: Bee colonies: Chinese honey bees (Apis cerana) cost 500-600 RMB per hive. Equipment: Hives, frames, and foundation sheets average 100 RMB per hive. Supplies: Feed (mainly sugar for winter) and medications total ≤30 RMB/hive annually. First-year cost per hive: ≈630 RMB (excluding labor) Subsequent years: ≈30 RMB/hive (no need to repurchase colonies or hives) 2. Profit Potential Analysis Key revenue comes from honey production: Average yield: 10 jin/hive/year (range: 5-15 jin for Chinese bees) Market price: 150 RMB/jin (range: 100-200 RMB for raw local honey) Annual revenue per hive: 1,500 RMB Net profit: – Year 1: 870 RMB (after 630 RMB investment) – Subsequent years: 1,470 RMB 3. Factors Affecting Honey Yield Two critical factors influence production: Weather conditions: Continuous rain or strong winds during nectar flow periods can reduce yields by 30-50%. Beekeeping expertise: – Novices: May produce <5 jin/hive – Experts using rotational apiary methods: >20 jin/hive 4. Market Price Dynamics Honey prices vary dramatically due to: Rarity: Pure local honey (土蜂蜜) ranges from 100-300 RMB/jin Regional differences: Urban markets vs. rural direct sales Certifications: Organic certification increases value by 40-60% 5. Skill Development Strategies Maximizing returns requires technical knowledge: Apiary management: A skilled keeper can manage 30-50 hives Potential earnings: 45,000-75,000 RMB/year Recommendations: 1. Start with 3-5 hives as side income 2. Attend local beekeeping workshops 3. Implement gradual scale-up after 2-3 years Critical Reminder: While beekeeping appears lucrative theoretically, success requires balancing three elements: Favorable…