Queen Cage: Essential Tool in Beekeeping

I. Definition and Overview
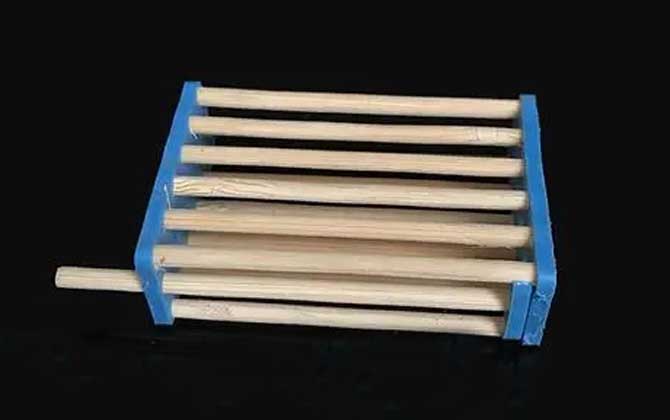
The queen cage is a specialized beekeeping tool designed to temporarily confine queen bees. Typically constructed from bamboo, wood, or plastic, this device features precisely calibrated gaps between its bars. These gaps are strategically sized between the thoracic thickness of queen bees and worker bees, allowing worker bees free access while securely containing the queen. Its primary applications include new queen introduction and controlled egg-laying management.
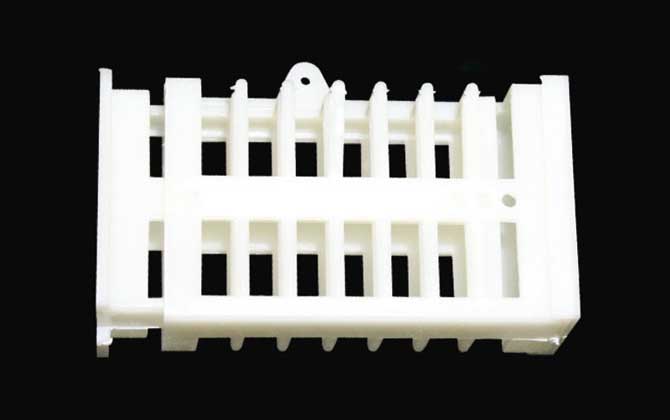
II. Design Principles
The cage’s effectiveness stems from distinct biological differences:
- Thoracic measurements: Queen bees (1.8-2.0mm) vs Worker bees (1.4-1.6mm)
- Bar spacing: 1.6-1.8mm (prevents queen escape)
- Material durability: Weather-resistant plastics or untreated hardwoods
This precision engineering enables continuous colony interaction while maintaining queen containment.
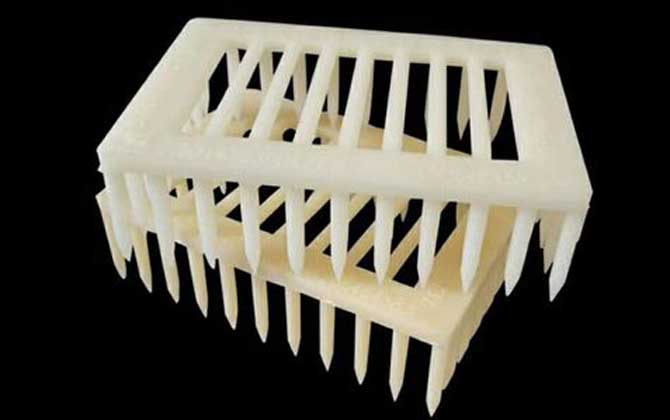

III. Primary Functions
Queen cages serve multiple critical roles:
- Safe queen introduction to new colonies
- Egg-laying regulation during honey flows
- Temporary queen isolation during disease treatment
- Queen banking for commercial operations
- Emergency queen protection during colony disturbances
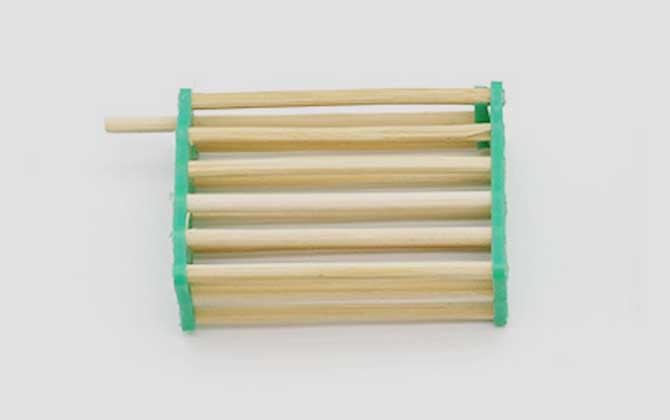

IV. Proper Usage Guidelines
For optimal results:
- Position cage on honeycomb with direct worker access
- Ensure adequate ventilation and feeding ports
- Limit confinement period (typically 3-7 days)
- Monitor worker interaction patterns
- Use smooth plastic cages to prevent leg damage
Critical Note: Always handle queens gently using specialized tools to prevent abdominal injury.
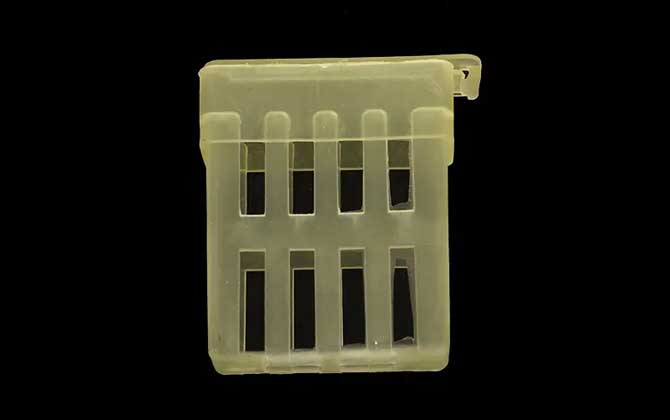

V. Practical Applications
1. Queen Introduction:
- Gradual scent integration over 24-72 hours
- Reduces worker rejection from 40% to <5%
- Enables controlled pheromone transfer
2. Egg-Laying Management:
- Increases honey production by 20-30% during flows
- Prevents brood competition during nectar dearth
- Facilitates colony population control
3. Queen Banking:
- Maintains backup queens with host colonies
- Allows emergency replacement within 24 hours
- Supports commercial pollination operations
VI. Maintenance Considerations
Proper care ensures longevity:
- Regularly clean with propolis solvent
- Inspect bar spacing monthly
- Disinfect between uses (5% acetic acid solution)
- Store in dry, pest-free environments
Modern innovations include RFID-tagged cages for tracking and temperature-regulated models for improved queen survival during transport.